Imagine waking up one morning to find your phone drained, your bank account tampered with, and private photos leaked online—all because of a silent malware attack you never saw coming. This is no longer a rare horror story but a growing threat in our increasingly mobile-first world.
As smartphones continue to function like pocket-sized computers, they’ve become prime targets for cybercriminals. In 2025, malware attacks have evolved—leveraging AI, zero-click vulnerabilities, and sophisticated social engineering. This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to identify signs of infection, avoid risky behaviors, and safeguard your smartphone from current and future malware threats.
With attackers becoming more strategic and technically skilled, securing your smartphone in 2025 has never been more crucial. This in-depth guide explores the latest mobile security threats, signs your device may be compromised, and effective strategies to keep your data protected.
Also Read: Infinix Note 50: List, Design and Specifications Surfaced on FCC Certification Site
Understanding Malware
Malware, short for malicious software, is any software designed to harm, exploit, or gain unauthorized access to a system. It comes in many forms—including viruses, spyware, ransomware, and trojans—and is used by hackers to access personal data, disrupt device functionality, or cause financial loss.
Each type of malware has its own method of operation, but the core objective remains the same: to compromise your security and exploit your information.
Major Smartphone Threats in 2025
AI-Powered Cyberattacks
Attackers are now using artificial intelligence to launch sophisticated, automated threats. AI can craft convincing phishing messages, making it easier to deceive users.
Deep fake and Audio Manipulation
Fraudsters can now create highly convincing fake videos and audio clips that mimic real individuals. These are used to deceive users into sharing private or financial information.
Zero-Click Malware
This type of malware doesn’t require any user interaction to infect a device. It exploits vulnerabilities in messaging apps or operating systems silently.
Expanded 5G and IoT Exposure
With more connected devices thanks to 5G and IoT integration, there are increased points of entry for attackers targeting smartphones.
Cloud-Based Threats
Storing sensitive data in the cloud is convenient, but it also attracts hackers targeting those platforms.
How Malware Enters Smartphones
Misleading Pop-Ups
Pop-up ads or alerts claiming your phone is infected or offering prizes are often traps that lead to malware installation.
Phishing and Smishing Scams
Fake emails or text messages disguised as official communication can lure users into clicking malicious links or downloading infected files.
Using Outdated Software
Delayed updates can leave your device exposed to known security flaws.
Installing Apps from Unknown Sources
Third-party apps not vetted by official stores often carry hidden malicious code.
Unsecured Websites
Visiting fake or insecure sites can unknowingly lead to device compromise.
Effective Protection Measures
Approach Mobile Security Like Desktop SecurityOnly install trusted applications and be cautious with permissions.
Avoid Public Wi-Fi for Sensitive Transactions
Public networks are easily exploitable. Use a VPN for secure browsing.
Workplace Security with BYOD Policies
Organizations should enforce strict security protocols for employee-owned devices.
Always Keep Your OS and Apps Updated
Updates often patch security vulnerabilities. Enable automatic updates.
Encrypt Device Data
Encrypting your phone protects your files even if the device is stolen.
Download Apps with Caution
Check reviews, developer reputation, and requested permissions before installing any app.
Use Strong Passwords and Biometrics
Combine complex passwords with fingerprint or facial recognition for layered security.
Avoid Sending Sensitive Info via Text
SMS can be intercepted. Use encrypted messaging platforms instead.
Check for Secure Site Indicators
Only input sensitive info on websites with HTTPS and a secure padlock icon.
Unique Android-Specific Risks
Flexibility Comes at a Cost: Android’s open nature makes it more customizable, but also more vulnerable to threats.
Delayed Manufacturer Updates: Some manufacturers are slow to roll out crucial security patches.
Side loading Risk: Manually installing apps from external sources bypasses built-in security measures.
Excessive Permissions: Be cautious of apps that request more access than necessary.
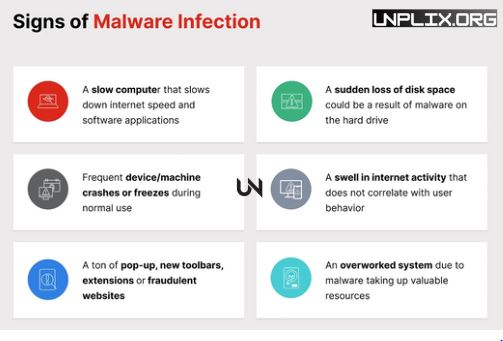
Red Flags of Malware Infection
- Unusual Data Consumption Malware often operates in the background, consuming large amounts of data.
- Faster Battery Drain An infected phone may run unnecessary processes, draining power quickly.
- Intrusive Ads and Pop-Ups Adware often floods your device with unwanted advertisements.
- New Apps You Didn’t Install Random apps appearing without your knowledge may indicate a compromise.
- Sluggish Performance or Freezing Malware can affect your phone’s speed and stability.
- Demand for Ransom Ransomware will lock your device and demand payment to restore access.
- Unusual Messages or Calls Malware may send unauthorized texts or make calls from your device.
Common Methods of Malware Spread
- Email Attachments Disguised as Documents
- Fake Links in Social Media or SMS
- Malvertising in Banner Ads
- Infected External Devices (USB)
- Exploiting Missed Updates
Malware Removal Techniques
- Scan with a Trusted Antivirus: a reputable app to scan and remove threats.
- Boot into Safe Mode: This prevents third-party apps from running, allowing for easier threat removal.
- Remove Suspicious Applications: Uninstall unknown or recently added apps.
- Clear Cache and Download History: Eliminate temporary files that may contain hidden threats.
- Use Mobile Device Management (MDM): Businesses can remotely secure or wipe compromised devices.
- Factory Reset if Necessary: As a last resort, reset your device to its original settings after backing up your data.
Long-Term Defense Strategies
- Regularly audit installed apps
- Monitor data and battery use
- Don’t root or jailbreak your phone
- Activate remote wipe features
- Stay updated on current cybersecurity threats
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What’s the most common malware in 2025?
Zero-click malware that requires no user action is on the rise.
How do I spot a malicious app?
Watch for apps with poor ratings, excessive permissions, and odd behavior.
Can a factory reset remove all malware?
It removes most threats, but extremely sophisticated malware may persist.
Is antivirus software necessary on phones?
Yes, it helps detect and stop threats before they cause harm.
Can malware access my banking info?
Yes, it can steal credentials, OTPs, and other sensitive data.
How can I avoid unsafe apps?
Use official app stores, read reviews, and limit permissions.
Is iPhone safe from malware?
iOS is more secure, but it’s not invulnerable.
Does a VPN block malware?
No, VPNs protect data transmission but don’t prevent downloads of infected files.
Why are software updates important?
Updates fix known vulnerabilities that hackers exploit.
How can I stay informed about threats?
Subscribe to cybersecurity blogs or enable alerts from your security app.
Final Thoughts
As mobile threats continue to grow in sophistication, taking control of your smartphone’s security is essential. By understanding the risks, recognizing suspicious behavior, and adopting preventive habits, you can reduce your exposure to mobile malware in 2025.
Don’t wait for a breach to occur—protect your digital life today. Your smartphone isn’t just a communication device anymore; it’s a gateway to your identity, finances, and privacy. Treat it accordingly.